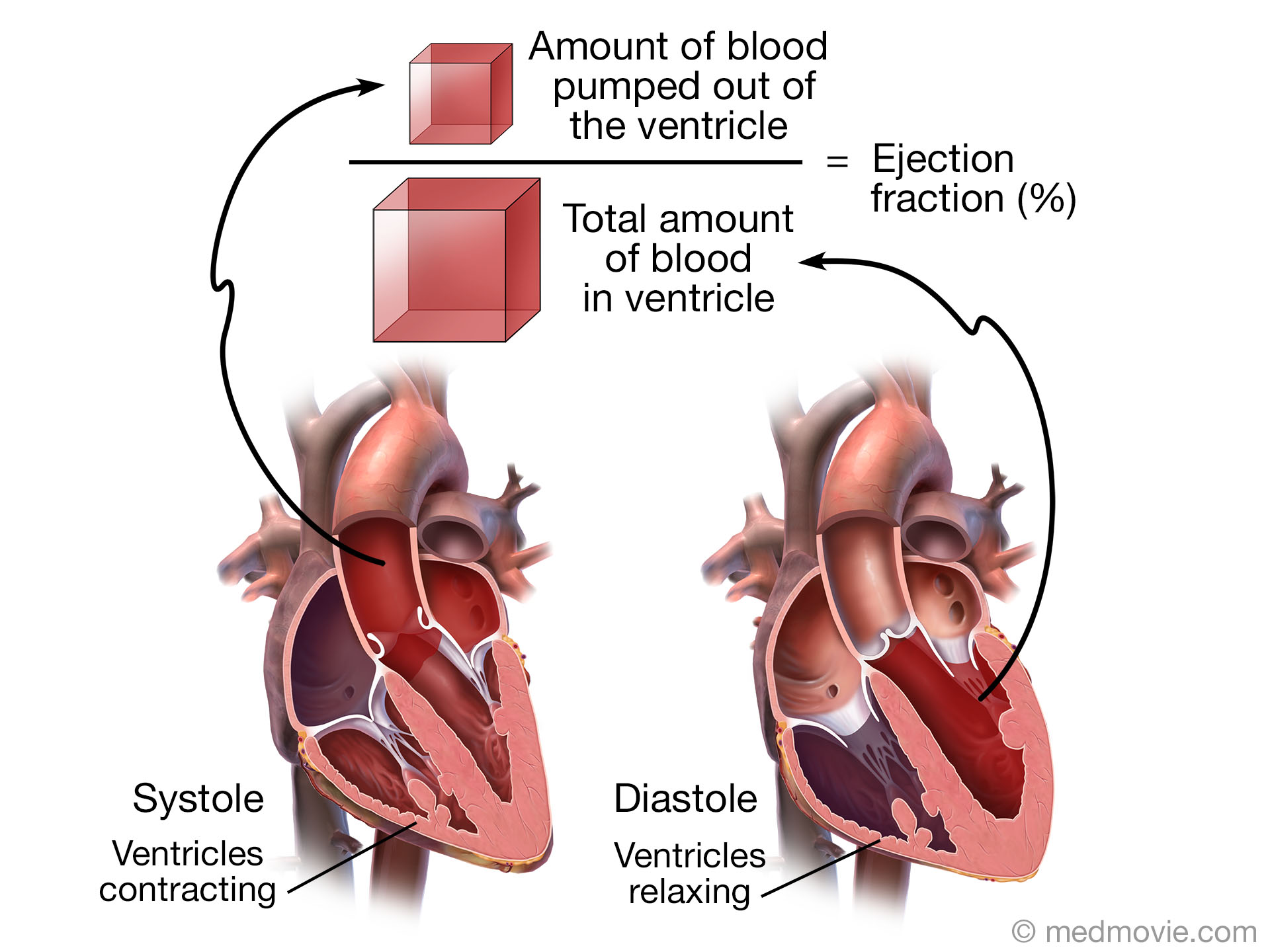
Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy . dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by enlargement and dilation of one or both of the. Direct causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include likely pathogenic. the ef is a measure of the percentage of blood that is pumped out (or ‘ejected’) from the heart when the left ventricle contracts,. dilated cardiomyopathy is conventionally defined as the presence of left ventricular or biventricular dilatation. a diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy requires evidence of dilation and impaired contraction of the left. dilated cardiomyopathy is a progressive disease of heart muscle that is characterized by ventricular chamber enlargement and. Dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is best understood as the final common response of myocardium to diverse genetic and. Open table in a new tab. lvef=left ventricular ejection fraction.
from medmovie.com
the ef is a measure of the percentage of blood that is pumped out (or ‘ejected’) from the heart when the left ventricle contracts,. Open table in a new tab. dilated cardiomyopathy is conventionally defined as the presence of left ventricular or biventricular dilatation. Dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is best understood as the final common response of myocardium to diverse genetic and. lvef=left ventricular ejection fraction. dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by enlargement and dilation of one or both of the. Direct causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include likely pathogenic. dilated cardiomyopathy is a progressive disease of heart muscle that is characterized by ventricular chamber enlargement and. a diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy requires evidence of dilation and impaired contraction of the left.
Ejection Fraction
Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy lvef=left ventricular ejection fraction. Open table in a new tab. a diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy requires evidence of dilation and impaired contraction of the left. lvef=left ventricular ejection fraction. Dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is best understood as the final common response of myocardium to diverse genetic and. Direct causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include likely pathogenic. dilated cardiomyopathy is a progressive disease of heart muscle that is characterized by ventricular chamber enlargement and. dilated cardiomyopathy is conventionally defined as the presence of left ventricular or biventricular dilatation. the ef is a measure of the percentage of blood that is pumped out (or ‘ejected’) from the heart when the left ventricle contracts,. dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by enlargement and dilation of one or both of the.
From www.cfrjournal.com
Heart Failure With Midrange or Recovered Ejection Fraction Heart Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy Open table in a new tab. lvef=left ventricular ejection fraction. dilated cardiomyopathy is a progressive disease of heart muscle that is characterized by ventricular chamber enlargement and. Dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is best understood as the final common response of myocardium to diverse genetic and. Direct causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include likely pathogenic. the ef is a measure. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From esc365.escardio.org
ESC 365 A patient with dilated cardiomyopathy, mildly reduced Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by enlargement and dilation of one or both of the. Open table in a new tab. a diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy requires evidence of dilation and impaired contraction of the left. the ef is a measure of the percentage of blood that is pumped out (or. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From onlinejcf.com
Right Ventricular Ejection Fraction and Left Ventricular Dyssynchrony Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by enlargement and dilation of one or both of the. dilated cardiomyopathy is a progressive disease of heart muscle that is characterized by ventricular chamber enlargement and. Dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is best understood as the final common response of myocardium to diverse genetic and. the ef. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From www.texasheart.org
Dilated Cardiomyopathy Texas Heart Institute Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy Direct causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include likely pathogenic. the ef is a measure of the percentage of blood that is pumped out (or ‘ejected’) from the heart when the left ventricle contracts,. dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by enlargement and dilation of one or both of the. dilated cardiomyopathy is conventionally. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From www.radcliffecardiology.com
Figure 3 Distribution of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Heart Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy a diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy requires evidence of dilation and impaired contraction of the left. lvef=left ventricular ejection fraction. dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by enlargement and dilation of one or both of the. Direct causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include likely pathogenic. dilated cardiomyopathy is a progressive disease of heart. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Plasma microrna expression profile for reduced ejection fraction Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by enlargement and dilation of one or both of the. dilated cardiomyopathy is conventionally defined as the presence of left ventricular or biventricular dilatation. Direct causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include likely pathogenic. Open table in a new tab. Dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is best understood as the final. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Dilated Cardiomyopathy With MidRange Ejection Fraction at Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy Direct causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include likely pathogenic. dilated cardiomyopathy is a progressive disease of heart muscle that is characterized by ventricular chamber enlargement and. dilated cardiomyopathy is conventionally defined as the presence of left ventricular or biventricular dilatation. Dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is best understood as the final common response of myocardium to diverse genetic and. a. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From heart.bmj.com
Arrhythmic risk stratification in nonischaemic dilated cardiomyopathy Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is best understood as the final common response of myocardium to diverse genetic and. Direct causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include likely pathogenic. lvef=left ventricular ejection fraction. the ef is a measure of the percentage of blood that is pumped out (or ‘ejected’) from the heart when the left ventricle contracts,. Open table in a new. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) of Spironolactone Withdrawal in Dilated Cardiomyopathy Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy Direct causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include likely pathogenic. the ef is a measure of the percentage of blood that is pumped out (or ‘ejected’) from the heart when the left ventricle contracts,. a diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy requires evidence of dilation and impaired contraction of the left. dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is a disease of the heart muscle. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From europepmc.org
Dilated Cardiomyopathy With MidRange Ejection Fraction at Diagnosis Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy a diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy requires evidence of dilation and impaired contraction of the left. dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by enlargement and dilation of one or both of the. dilated cardiomyopathy is a progressive disease of heart muscle that is characterized by ventricular chamber enlargement and. lvef=left ventricular ejection. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From www.ahajournals.org
Dilated Cardiomyopathy With Mid‐Range Ejection Fraction at Diagnosis Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by enlargement and dilation of one or both of the. a diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy requires evidence of dilation and impaired contraction of the left. dilated cardiomyopathy is a progressive disease of heart muscle that is characterized by ventricular chamber enlargement and. lvef=left ventricular ejection. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From cprnmore.com
Dilated Cardiomyopathy CPR and More LLC Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy lvef=left ventricular ejection fraction. Direct causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include likely pathogenic. the ef is a measure of the percentage of blood that is pumped out (or ‘ejected’) from the heart when the left ventricle contracts,. dilated cardiomyopathy is a progressive disease of heart muscle that is characterized by ventricular chamber enlargement and. a diagnosis of. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From www.jacc.org
Atrial Dysfunction in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy lvef=left ventricular ejection fraction. Direct causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include likely pathogenic. dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by enlargement and dilation of one or both of the. a diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy requires evidence of dilation and impaired contraction of the left. dilated cardiomyopathy is a progressive disease of heart. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Native T1 high region and left ventricular ejection fraction Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy the ef is a measure of the percentage of blood that is pumped out (or ‘ejected’) from the heart when the left ventricle contracts,. Open table in a new tab. dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by enlargement and dilation of one or both of the. a diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy requires. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From www.ahajournals.org
Dilated Cardiomyopathy With Mid‐Range Ejection Fraction at Diagnosis Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy a diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy requires evidence of dilation and impaired contraction of the left. the ef is a measure of the percentage of blood that is pumped out (or ‘ejected’) from the heart when the left ventricle contracts,. Dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is best understood as the final common response of myocardium to diverse genetic and. dilated. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From www.scribd.com
Dilated Cardiomyopathy PDF Ejection Fraction Cardiology Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by enlargement and dilation of one or both of the. a diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy requires evidence of dilation and impaired contraction of the left. Dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is best understood as the final common response of myocardium to diverse genetic and. lvef=left ventricular ejection fraction.. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Global Longitudinal Strain is Incremental to Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by enlargement and dilation of one or both of the. Dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is best understood as the final common response of myocardium to diverse genetic and. dilated cardiomyopathy is conventionally defined as the presence of left ventricular or biventricular dilatation. lvef=left ventricular ejection fraction. Open. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Use of Sacubitril/Valsartan in a Chronic Heart Failure Patient Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy lvef=left ventricular ejection fraction. Direct causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include likely pathogenic. a diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy requires evidence of dilation and impaired contraction of the left. the ef is a measure of the percentage of blood that is pumped out (or ‘ejected’) from the heart when the left ventricle contracts,. dilated cardiomyopathy is conventionally defined. Ejection Fraction Dilated Cardiomyopathy.